Utilizing Technology to Effectively Manage Mosquitoes
A geographic information system, GIS, is a set of tools that allow us to visualize, question, analyze, and interpret data. By creating maps, reports, or charts, you can reveal relationships, patterns, or trends in data that often play a significant role in decision making.
GIS is designed to capture data and store it in various digital formats (individual files, databases, geodatabases, etc.) so that data can be edited and managed with ease. Most industries and businesses of all sizes can benefit from GIS to improve record keeping, provide guidance on where to apply financial and human resources, and support communication and education efforts with employees and customers. The technology offers a variety of data to assist in decision-making, which is vital within industries that manage time-sensitive projects and/or services where public education and public health are a concern.
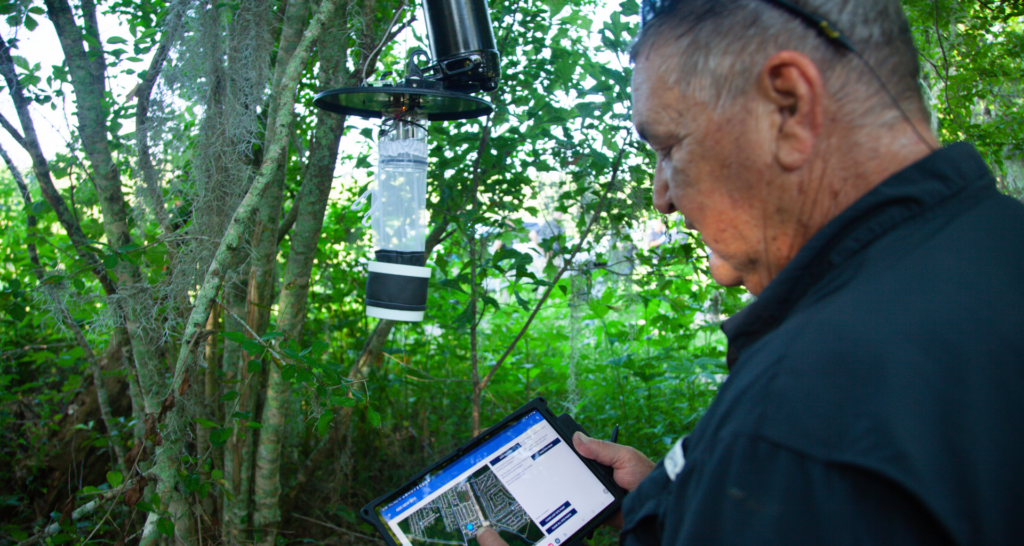

What Role Can GIS Technology Play in Effective Mosquito Control?
A keystone of the Integrated Mosquito Management (IMM) approach is managing data. GIS data can be analyzed and presented in a visual manner that many find easier to understand. The greatest resource that is provided as a result of GIS technology is a map! Maps are a beautiful way to highlight data. The visual aids combine findings and give it context that is customized for a specific audience. Additionally, customers can be provided with activity reports on a regular basis depending on their needs. As part of an IMM program GIS technology can help:
Track Larval Habitats and Larval Control Applications
Field technicians can use GPS coordinates to collect data related to larval habitats and larvicide applications. Data can include marking a location that was visited, noting if a location had larval activity, or tracking how much product was applied to a given area.
Process Surveillance and Disease Monitoring Data
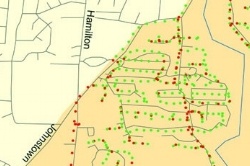 Using GIS can provide a clear idea of what is happening in the mosquito populations in any given area. First, trap locations can be recorded and added to a database. Next, mosquito counts and species identified can be populated for each location. Then, disease testing can be inputted for each trap and mapped on an ongoing basis. Additionally, service requests can be logged and mapped to help identify problem areas.
Using GIS can provide a clear idea of what is happening in the mosquito populations in any given area. First, trap locations can be recorded and added to a database. Next, mosquito counts and species identified can be populated for each location. Then, disease testing can be inputted for each trap and mapped on an ongoing basis. Additionally, service requests can be logged and mapped to help identify problem areas.
Determine Adulticide Application and Treatment Exclusion Areas
By tracking the mosquito populations, managers can make educated decisions on whether control measures are needed as well as when and where to make adulticide applications. The data allows mosquito control technicians to set parameters and load a base map for each mosquito application mission. During a ground mission, a technician’s truck has a GPS controlled variable flow Ultra-Low Volume (ULV) sprayer and a PC within the cab that displays a moving map and mission database to record the GIS data. All aspects of adulticide applications (ground or aerial) can be recorded including but not limited to time and date of application, the application rate, the product utilized, the amount of product applied, and the specific route with notes on exclusion areas.
In addition to the practical applications, in the day-to-day operations of an IMM program, GIS can assist in:
Regulatory Compliance
To maintain individual and corporate compliance and licensing with multiple government agencies and jurisdictions is a daunting task. By accurately recording and mapping all aspects of a program, maps can be used to assure regulatory compliance and streamline requirements for initiatives like NPDES permitting.
Inventory Management
When ULV application equipment is coupled with GPS tracking units and on-board GIS monitoring systems, accurate chemical use is recorded. This allows program managers to know exactly how much adulticide is being used during every spray mission, which in turn provides them with the data they need to manage their product inventory efficiently. In larvicide applications, GIS data provides accurate area measurements so technicians know how much product to apply at any given site and managers know how much product they need to have on hand to treat all the sites in their program.
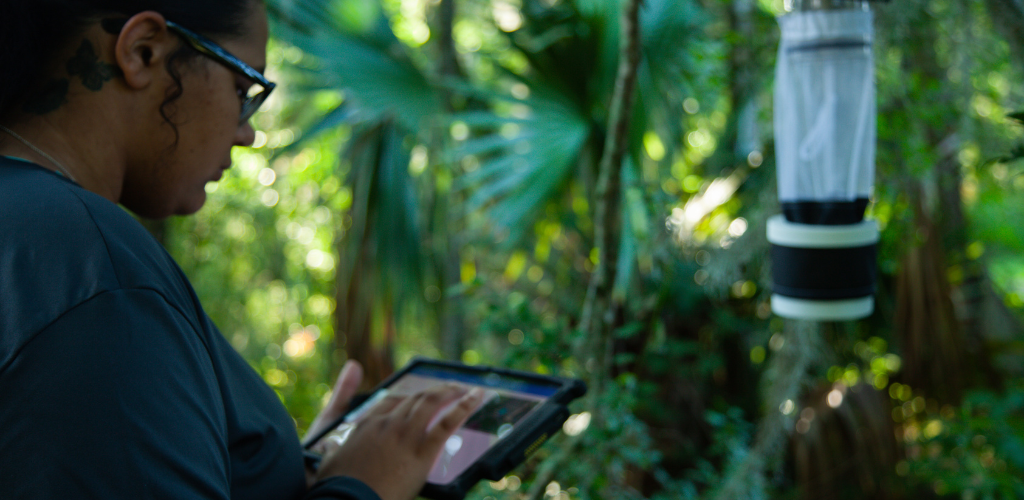

Public Education
By mapping public health risks, associated with disease monitoring in mosquito populations, GIS can support a community’s efforts to communicate if there is a mosquito-borne disease concern in a given area.
Emergency Response
Federal, state, and local governments use GIS to aid in emergency response efforts. GIS has played an integral role in controlling mosquito outbreaks after tropical storms, hurricanes, and intense flooding.
Utilizing GIS to Drive More Effective IMM Programs
GIS can be utilized in every facet of an integrated mosquito management program. With ongoing advances in technology, the possibilities of GIS improving the efforts to protect public health from mosquito-borne diseases are endless.
Contact Us to Learn More About Effective Mosquito Prevention Strategies:
 Since 1992, Vector Disease Control International (VDCI) has taken pride in providing municipalities, mosquito abatement districts, industrial sites, planned communities, homeowners associations, and golf courses with the tools they need to run effective mosquito control programs. We are determined to protect the public health of the communities in which we operate. Our mosquito control professionals have over 100 years of combined experience in the field of public health, specifically vector disease control. We strive to provide the most effective and scientifically sound mosquito surveillance and control programs possible based on an Integrated Mosquito Management approach recommended by the American Mosquito Control Association (AMCA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). VDCI is the only company in the country that can manage all aspects of an integrated mosquito management program, from surveillance to disease testing to aerial application in emergency situations.
Since 1992, Vector Disease Control International (VDCI) has taken pride in providing municipalities, mosquito abatement districts, industrial sites, planned communities, homeowners associations, and golf courses with the tools they need to run effective mosquito control programs. We are determined to protect the public health of the communities in which we operate. Our mosquito control professionals have over 100 years of combined experience in the field of public health, specifically vector disease control. We strive to provide the most effective and scientifically sound mosquito surveillance and control programs possible based on an Integrated Mosquito Management approach recommended by the American Mosquito Control Association (AMCA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). VDCI is the only company in the country that can manage all aspects of an integrated mosquito management program, from surveillance to disease testing to aerial application in emergency situations.

